The manned flight mission of Shenzhou 15 has achieved complete success
At 21:29 on June 3, 2023, the Shenzhou-15 manned spacecraft successfully separated from the space station complex. Before separation, the crew of Shenzhou-15 astronauts, with the cooperation of ground personnel, completed various pre evacuation tasks such as setting the status of the space station assembly, organizing and transmitting experimental data, and clearing and transferring orbital materials. They also completed the handover of work with the crew of Shenzhou-16.
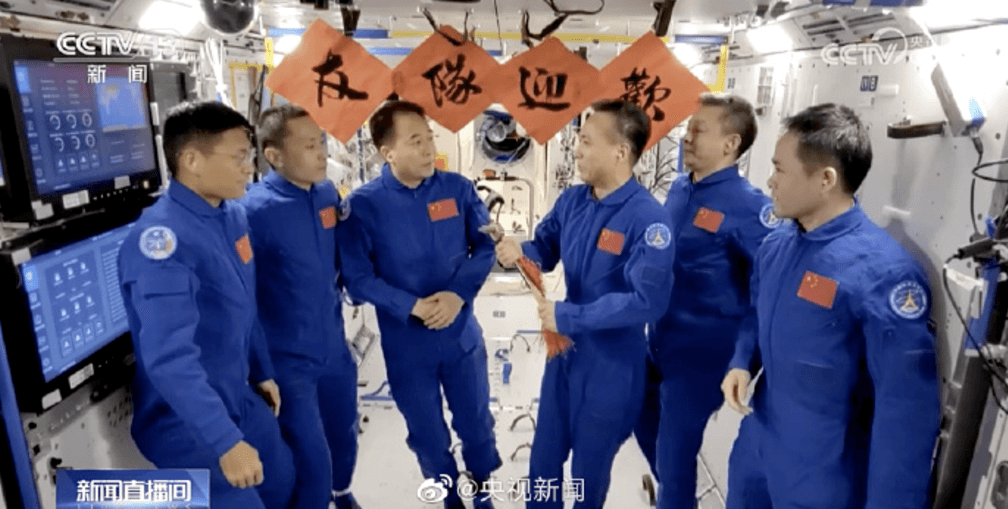

The return capsule of Shenzhou-15 manned spacecraft successfully landed at the Dongfeng landing site
At 6:33 am on June 4th, the return capsule of the Shenzhou-15 manned spacecraft successfully landed at the Dongfeng landing site. The on-site medical supervision and insurance personnel confirmed that the astronauts Fei Junlong, Deng Qingming, and Zhang Lu were in good physical condition and arrived safely in Beijing on the afternoon of June 4th. After arriving in Beijing, the three astronauts will enter the quarantine and recovery period, undergo comprehensive medical examinations and health assessments, and arrange for rest. Afterwards, there will be a collective meeting with the news media in Beijing.
As the oldest average astronaut crew to perform missions to date, they not only broke the record for the number of outbound activities of a single Chinese astronaut crew, but also witnessed the historic moment of the comprehensive construction of the Chinese space station.

A New Record of Single Test Run Time for the Main Engine of China's Manned Lunar Rocket
In early June, the main engine of China's manned lunar landing rocket, a 130 ton pump rear swing liquid oxygen kerosene engine, developed by the Sixth Academy of China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation, completed its sixth test run after being put on stage, and the test was a complete success. The cumulative test run time of the engine reached 3300 seconds, once again setting a new record for a single test run of a 100 ton engine in China.

The Tianzhou-5 cargo spacecraft has completed its rendezvous and docking with the space station assembly again
The Tianzhou-5 cargo spacecraft, which had previously evacuated the space station assembly and had been flying independently in orbit for 33 days, completed its rendezvous and docking with the space station assembly again at 3:10 am Beijing time on June 6, 2023.

Release of the 37th batch of scientific exploration data from Chang'e-4
On June 6, 2023, the ground application system of the lunar exploration project publicly released the 37th batch of scientific data from Chang'e-4. The data released this time is provided by the ground application system, including 2.3GB of scientific data obtained from the 51st to 53rd lunar days (2023.1.15-2023.3.28) of the five scientific payloads carried on the Chang'e-4 lander and rover (Yutu 2 lunar rover).
The third batch of scientific exploration data released by Tianwen-1 and the 37th batch of scientific exploration data released by Chang'e-4
On June 6, 2023, the ground application system of the first Mars exploration mission publicly released scientific data obtained from 12 scientific payloads, including the high-resolution camera carried on the Tianwen-1 spacecraft, in December 2021. The total amount of data released in this batch is 128.2GB.
The Lijian-1 Yao-2 carrier rocket has been successfully launched
At 12:10 am on June 7, 2023, the Lijian-1 YJ-2 carrier rocket was successfully launched from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in China, using the 'one arrow 26 satellite' method to successfully launch the test satellite into the designated orbit. This batch of satellites is mainly used for technical validation experiments and commercial remote sensing information services.
This mission is the second flight of the Lijian 1 carrier rocket.

China has successfully launched the Longjiang-3 experimental satellite
At 10:35 am on June 9, 2023, China successfully launched the Longjiang-3 experimental satellite into orbit using the Kuaizhou 1A carrier rocket at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center. The satellite entered its intended orbit and the launch mission was a complete success. This satellite is mainly used for satellite communication and remote sensing technology verification.
This mission is the 20th flight of the Kuaishou 1A carrier rocket.
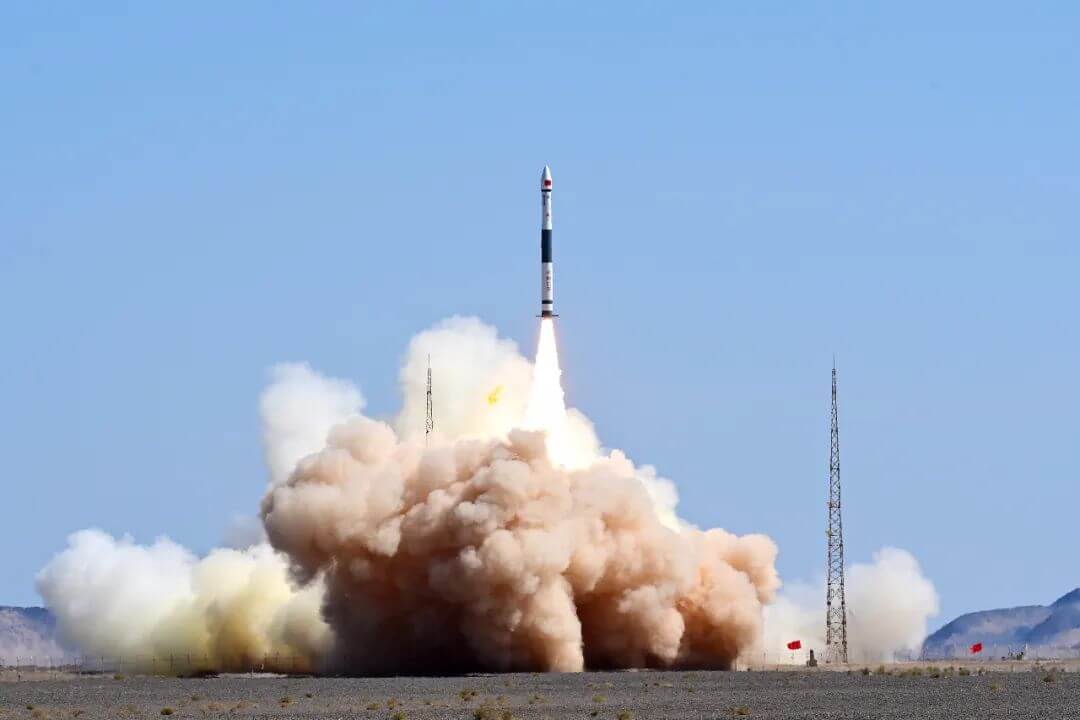

Tianbing Technology TH - Mengtian Module's first outbound payload installed in place
In early June, the Space Radiation Biology Exposure Experimental Device (hereinafter referred to as the Space Radiation Biology Device) of the Space Station's Mengtian Experimental Module was grabbed by a robotic arm and removed from the cargo airlock. It was successfully installed on the designated external exposure platform through a mid rotation and started up and operated normally.
The space radiation biology device is the first payload of the Mengtian module, used to conduct research on the biological effects of environmental factors such as space particle radiation on sample materials. It can meet the requirements of biological samples for timeliness, temperature, and other aspects during the extravehicular process, providing life support for scientific experimental biological samples. This is the first time in China that an extravehicular radiation biology exposure experiment has been conducted, which is of milestone significance for radiation biology and space science research.
China has successfully launched 41 satellites with a high resolution of 06A magnitude, including the Jilin-1 satellite
At 13:30 on June 15, 2023, China successfully launched 41 satellites, including Jilin-1 High Resolution 06A, using the Long March-2D carrier rocket from the Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center. The satellites entered the designated orbit and the launch mission was a complete success. This batch of satellites is mainly used to provide commercial remote sensing services and related technology validation.
This mission is the 476th flight of the Long March series of carrier rockets.
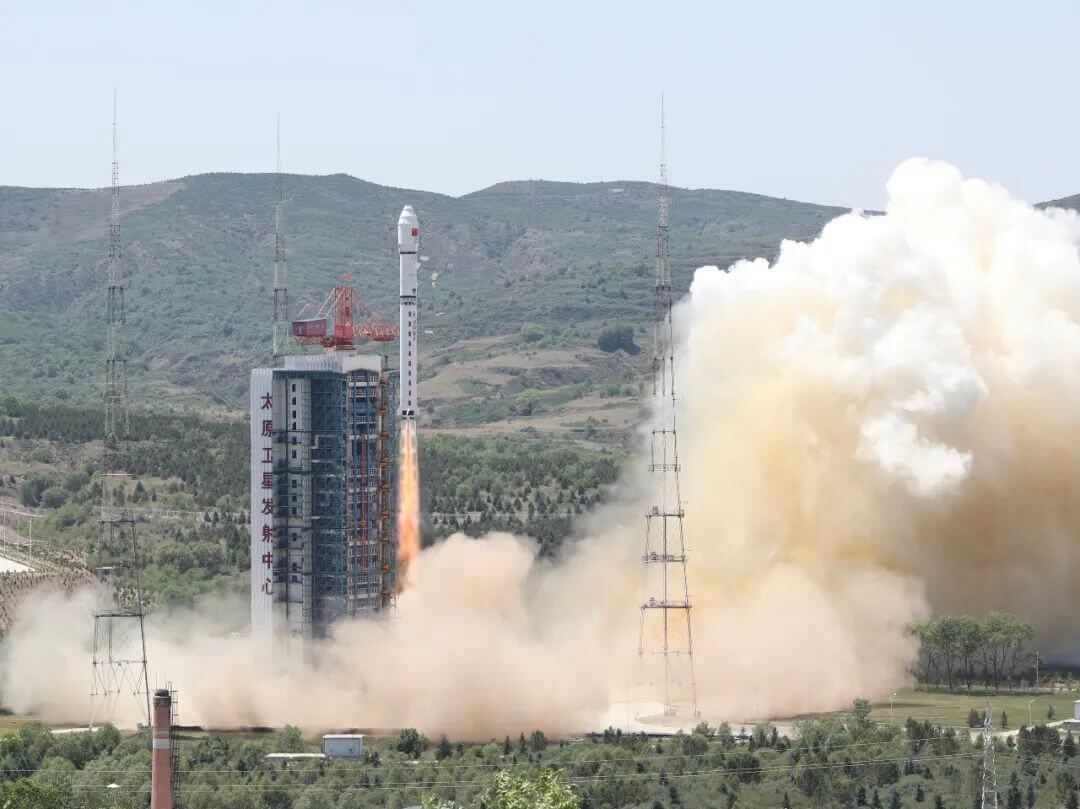

The interstage separation test of the Zhishenxing 1 liquid carrier rocket has been successfully completed!
In mid to early June, Xinghe Power Aerospace successfully completed the interstage separation test of the Zhishenxing 1 carrier rocket. During the experiment, all systems worked normally and the interstage segments were successfully separated, verifying the correctness of the interstage separation scheme. The experiment was a complete success!
The success of this inter stage separation test marks a solid step forward in the development of Zhishenxing 1. Other large-scale ground tests will be carried out in an orderly manner as planned.

The LHT-200 Hall thruster at Institute 510 of the Fifth Academy of Aerospace Science and Technology achieves stable operation with high performance and wide range
In mid to early June, the LHT-200 (12.5 kW) high-power Hall thruster developed by the 510 Institute of the Fifth Academy of China Aerospace Science and Technology Group Co., Ltd. was successfully ignited for the first time on a large electric propulsion vacuum test equipment, achieving high index and wide range stable operation.
High power Hall electric propulsion, as an important technological route in the international advanced space propulsion field, has good application prospects in various space missions such as manned spaceflight, cargo spacecraft, interstellar exploration, sampling and return. The LHT-200 Hall thruster is a key product in the field of technology at 510 Institute, characterized by high thrust, high specific impulse, wide working range, and high reliability. The development team has made unremitting efforts to overcome key technologies such as efficient thermal protection design, high-power high-voltage electrical insulation protection, efficiency improvement of thrusters based on magnetic field topology optimization design, and wide range power regulation. The first ignition test achieved key technical indicators under power conditions of 3-13 kilowatts, which is comparable to international advanced level products.
China has successfully launched and tested the 25th satellite
At 11:18 am on June 20, 2023, China successfully launched the Experiment 25 satellite into orbit using the Long March 6 carrier rocket at the Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center, and the launch mission was a complete success. This satellite is mainly used for conducting experiments on new earth observation technologies.
This mission is the 477th flight of the Long March series of carrier rockets.
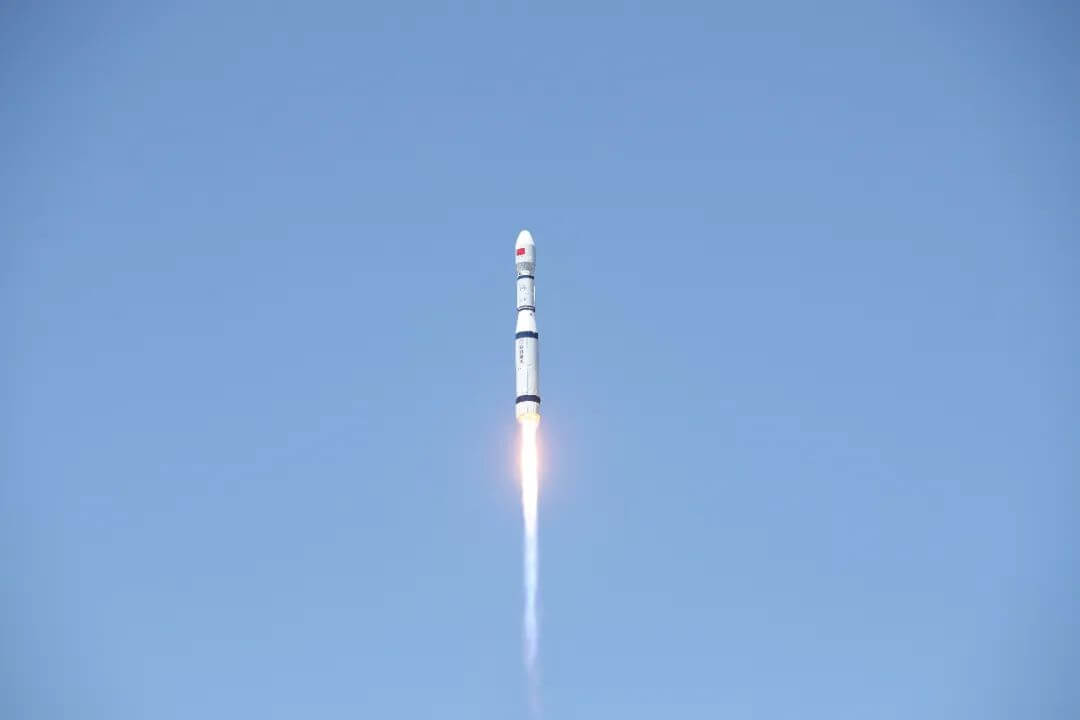

China's first low orbit broadband communication test constellation has completed its first offshore test
In mid June, staff from Galaxy Aerospace and multiple scientific research institutions boarded the 'Dianke 1' comprehensive test ship and completed the first offshore test of China's first low orbit broadband communication test constellation in the South China Sea. This test aims to verify the collaborative communication coverage ability of high and low orbit satellites and unmanned aerial vehicles, and accumulate data for achieving higher quality network communication in the distant sea in the future.
It is reported that in March 2022, the Xichang Satellite Launch Center successfully launched six low orbit broadband communication satellites developed by Galaxy Space into the designated orbit. These six satellites, together with the first launch satellite of Galaxy Space, formed the first low orbit broadband communication experimental constellation in China.
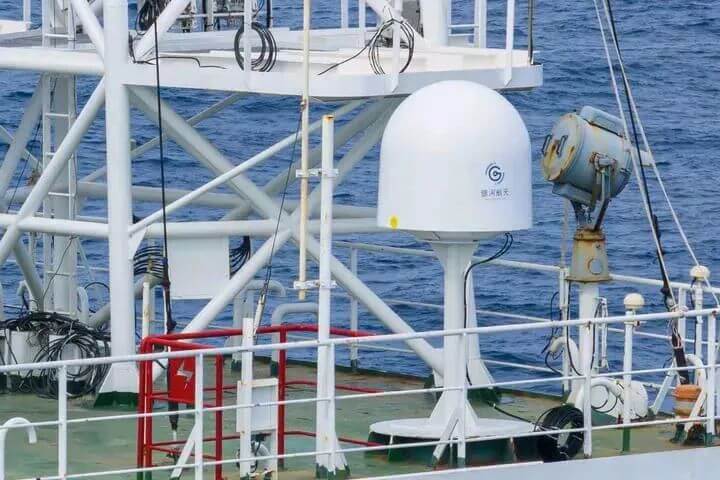

The Canglong 1 rocket engine has completed several system level test assessments
In mid June, the Canglong 1 liquid oxygen/LNG rocket engine (CL-1) independently developed and designed by Beijing Aerospace Propulsion Technology Co., Ltd. completed several system level ignition tests, with a focus on assessing the reliability and robustness of the engine ignition timing, the working characteristics of the thrust chamber and combustion engine under different working conditions and mixing ratios, and the working characteristics of the turbo pump under different working conditions. At the same time, the rationality and performance of other engine components were comprehensively verified, and the established test objectives were successfully achieved!
The 70 ton Canglong 1 (CL-1) engine uses liquid oxygen/LNG as propellant, and the system is a gas generator cycle. The engine has the ability to self pressurize and be reusable. This type of engine is mainly used in conjunction with the first stage and suborbital spacecraft of launch vehicles, and can also be extended to vacuum type to meet the requirements of the second stage of medium and large launch vehicles.
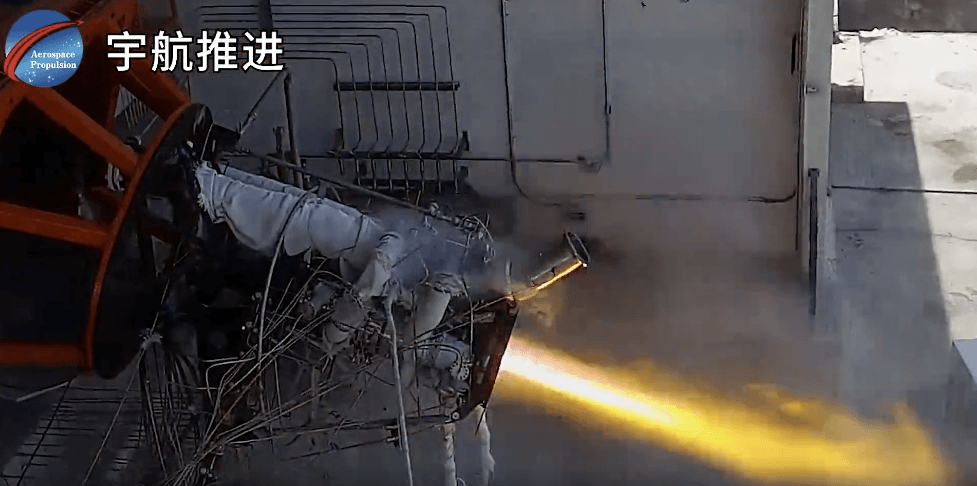

The electric propulsion engine of China's space station has achieved in orbit 'air exchange' for the first time
In mid June, with the cooperation of heaven and earth, the atmospheric cylinder of the electric propulsion system of the 'Tiangong' space station completed the in orbit installation task. For the first time, the 801 Institute of the Sixth Institute of China Aerospace Science and Technology Group Co., Ltd. used 'air exchange' instead of 'air replenishment' to supplement the electric propulsion propellant - xenon gas. The electric propulsion system of the space station equipped with large gas cylinders will greatly extend its service life, playing an important role in maintaining the long-term orbit and safe and stable flight of the space station.

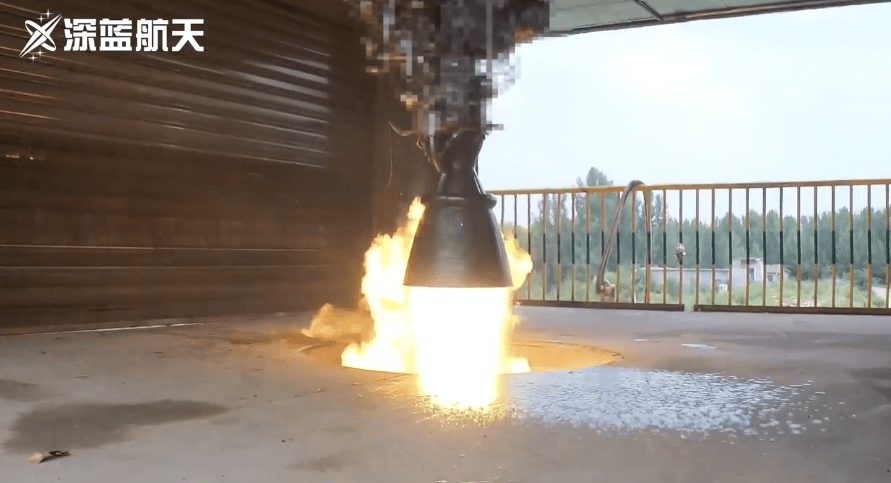
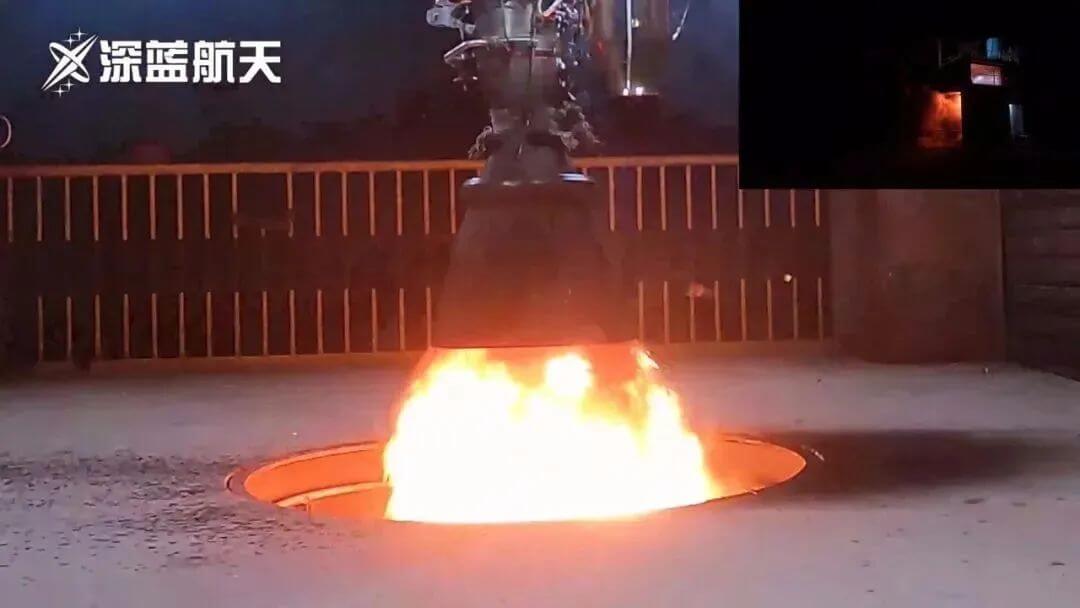
The new test bench at the Shenlan Aerospace Power Test Base has successfully completed the overall test bench test
In late June, the reusable engine 'Thunder-R1' independently developed by Deep Blue Aerospace achieved complete success in the vertical test bench test of the newly put into use vertical test bench. The same 'Thunder-R1' engine in this round of testing underwent several whole system tests, as well as dozens of different starting and ignition tests under different working conditions, once again highlighting the superior performance and stability of the 'Thunder-R1' engine's reusability.
The testing of the Thunder-R1 engine in this round and subsequent series will accumulate a large amount of data for the power system test, and also lay a solid foundation for the subsequent high-altitude vertical recovery flight test, orbital insertion and recovery first flight of the first stage of the Nebula 1 rocket. The subsequent test bench will continue to conduct regular engine testing and assessment to ensure the smooth implementation of the vertical recovery test for the first stage of the Nebula 1 rocket.

The separation tests of the first and second stages, as well as the second and third stages of the 'Gravitation-1' core in Dongfang Space, have been successfully completed
In late June, the 'Gravitation-1' carrier rocket of Dongfang Space completed the separation of the first and second stages of the core, as well as the separation of the second and third stages of the core. The impact conditions and various parameters during the separation process were obtained, verifying the adaptability of the product to the impact environment, the correctness of the separation scheme design, the coordination of separation timing actions, the reliability of the separation device operation, and the safety of the separation process. The experimental measurement results were consistent with the simulation predictions.
Both experiments used a composite low-cost buffering scheme, and the test pieces were recovered. The recovered test pieces can be further used for other experiments. As the world's first three-stage and half configuration solid rocket, the successful separation test between the two secondary phases marks the end of the ground verification work before the first flight of Gravitation-1. The company is making every effort to ensure the success of the first flight.

Deep Blue Aerospace's 'Thunder-R1' engine has once again undergone a complete test drive, entering the normalized testing phase
On June 29, 2023, the reusable engine 'Thunder-R1' of Deep Blue Aerospace conducted another full system test and achieved complete success. The 'Thunder-R1' has entered the normal testing stage. The Thunder-R1 remains consistently stable in performance, igniting, starting, and shutting down according to the predetermined procedures. The test conditions are good, and all indicators meet the design requirements.
In this test drive, shareholders of Deep Blue Aerospace also visited the New Power Test Base to witness the stunning effect of the entire engine test up close. The subsequent 'Thunder-R1' engine will undergo a series of tests, including three ignition cycles, operating condition deviation, and reliability verification, to ensure the smooth progress of the first sub stage vertical recovery test of the 'Nebula 1' rocket in the second half of the year.