The Chang'e-5 team won the Lawrence Team Award!
In an orbit over 400 kilometers away from Earth, the Chinese space station has traveled through the sky, becoming one of the important milestones in China's aerospace industry. Looking at the northeast corner of our country, a space environment ground simulation device called the 'Ground Space Station' was officially completed in early July and entered the trial operation stage. Many indicators have reached the world's leading level.
As the first large-scale scientific device in China's aerospace field, the Ground Space Station is the first comprehensive research device in the world that has the most comprehensive environmental factors and can achieve multi-scale and cross scale environmental effects research. It will contribute wisdom and strength to the development of China's aerospace industry and human space exploration.
The Ground Space Station is located in the Science and Technology Innovation City of Harbin New Area, Heilongjiang Province, and was jointly constructed by Harbin Institute of Technology and China Aerospace Science and Technology Group. In the construction of the park, there are four experimental buildings: one large and three small. The first large refers to the space comprehensive environment experimental building, and the third small refers to the space plasma science experimental building, space magnetic environment science experimental building, and animal culture room.

The fourth batch of scientific exploration data released by Tianwen-1
On July 3, 2023, the ground application system of the first Mars exploration mission publicly released scientific data obtained by 12 scientific payloads, including the high-resolution camera carried on the Tianwen-1 spacecraft, in 2022. The total amount of data released in this batch is 1563.4GB.

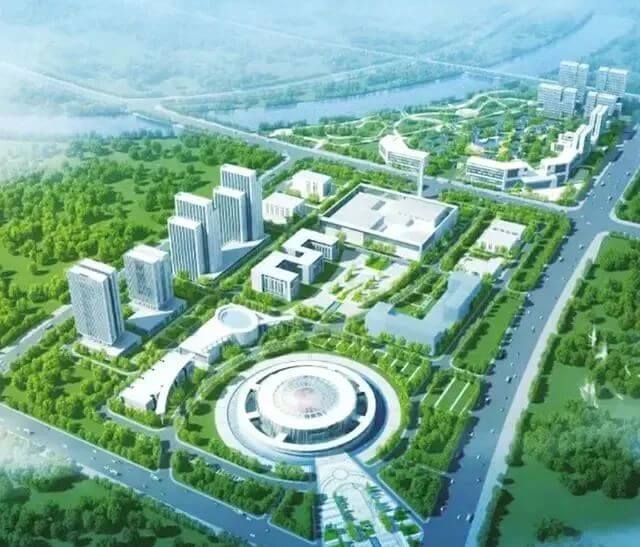
The verification rocket power system test of the Starry Glory Hyperbolic 2 has been successfully completed
On July 5, 2023 at 16:00, the power system test of the Starry Glory Hyperbolic 2 (SQX-2Y) rocket was successfully completed.
The SQX-2Y rocket is a type of verification rocket used to verify the vertical recovery and reuse of liquid oxygen methane reusable launch vehicles. It adopts a full size arrow body diameter of 3.35m and can be equipped with one or more self-developed Focus One engines according to mission requirements to verify the true flight and return conditions of the first stage of the reusable launch vehicle.
The SQX-2Y rocket power system test is an important and critical large-scale ground test before the Hyperbolic 2 verification flight test, focusing on assessing the coordination, matching, and safety of the rocket power system, electrical system, and other systems, as well as the correctness and effectiveness of the launch site process. The successful completion of this test mission has laid a solid foundation for the SQX-2Y rocket to conduct vertical takeoff and landing flight tests.

Jilin No.1 achieves high-speed satellite ground laser communication
In the first ten days of July, Jilin Changguang Satellite, using the self-developed satellite 'Jilin No. 1' MF02A04, carried out a satellite ground laser high-speed communication experiment with the Aerospace Information Innovation Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and achieved success, marking that China has realized the application of satellite ground laser high-speed communication engineering, laying the foundation for the expansion of China's satellite ground communication system from microwave to laser.

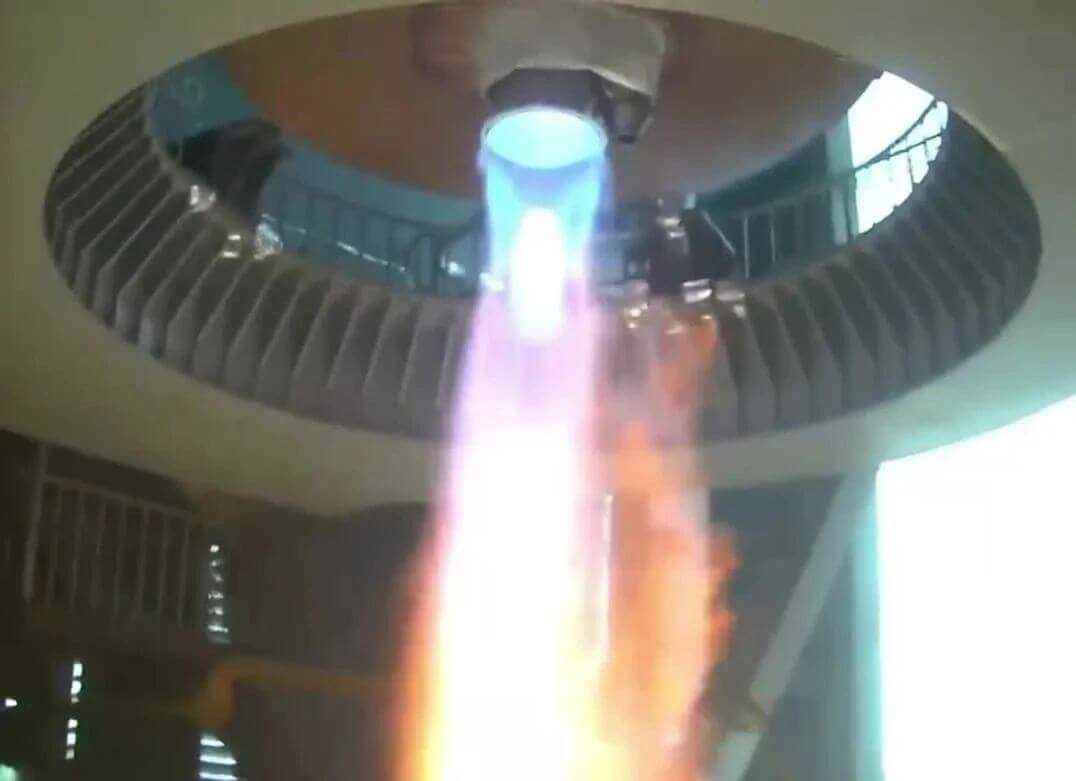
China Successfully Launches Satellite Internet Technology Test Satellite
At 19:00 on July 9, 2023, China successfully launched the satellite Internet technology test satellite by using the Long March 2C carrier rocket at Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center. The satellite successfully entered the scheduled orbit, and the launch mission was a complete success.
This mission is the 478th flight of the Long March series of carrier rockets.
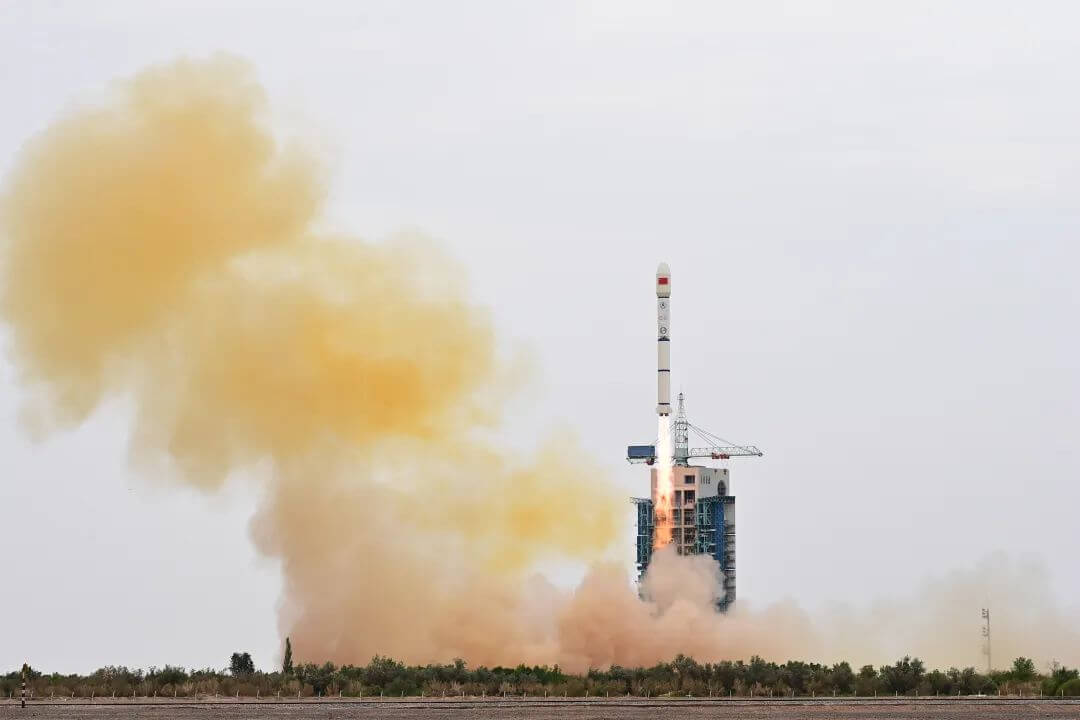

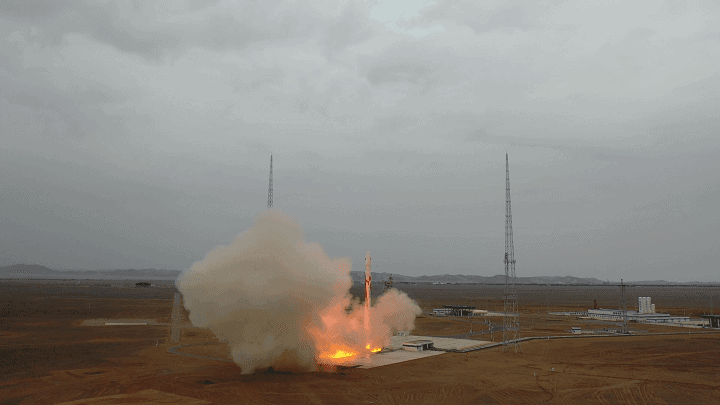
The successful launch of the Zhuque 2 Yao 2 carrier rocket
At 9:00 am on July 12, 2023, the Zhuque 2 Yao 2 carrier rocket was launched from China's Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center and completed the flight mission according to the procedure, achieving a complete success in the launch mission.
This mission is the second flight of the Zhuque 2 carrier rocket.
Preliminary plan for China's manned moon landing announced
On July 12th, Zhang Hailian, Deputy Chief Engineer of the China Manned Space Engineering Office, revealed at the 9th China (International) Commercial Aerospace Summit Forum held in Wuhan that China plans to achieve manned landing on the moon for scientific exploration before 2030. Afterwards, China will explore the construction of a lunar research and testing station to carry out systematic and continuous lunar exploration and related technology testing and verification.
At present, the preliminary plan for manned lunar landing in China is:
Two carrier rockets were used to transport the lunar lander and manned spacecraft to the Earth Moon transfer orbit. The spacecraft and lander intersected and docked in the lunar orbit, and astronauts entered the lunar lander from the spacecraft. The level of 'zero error code' and 'zero packet loss' has achieved all established goals, and the in orbit test of high-speed optical switching technology has achieved complete success.
Afterwards, the lunar lander will descend and land in the designated area on the lunar surface, and astronauts will land on the moon to conduct scientific investigations and sample collection.
After completing the established mission, astronauts will ascend to the lunar orbit and rendezvous with the spacecraft on the lander, and return to Earth with samples on the spacecraft.
To complete this task, Chinese researchers are developing equipment such as the Long March 10 carrier rocket, a new generation of manned spacecraft, lunar landers, lunar suits, and manned lunar rovers.

China has successfully launched the Tianmu 1 meteorological constellation 07-10 stars
At 11:20 am Beijing time on July 20, 2023, China successfully launched the Tianmu 1 Meteorological Constellation 07-10 using the Kuaizhou-1A carrier rocket at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center. The satellite was successfully placed into the designated orbit and the launch mission was a complete success. This satellite is mainly used to provide commercial meteorological data services.
This mission is the 21st flight of the Kuaishou 1A carrier rocket.

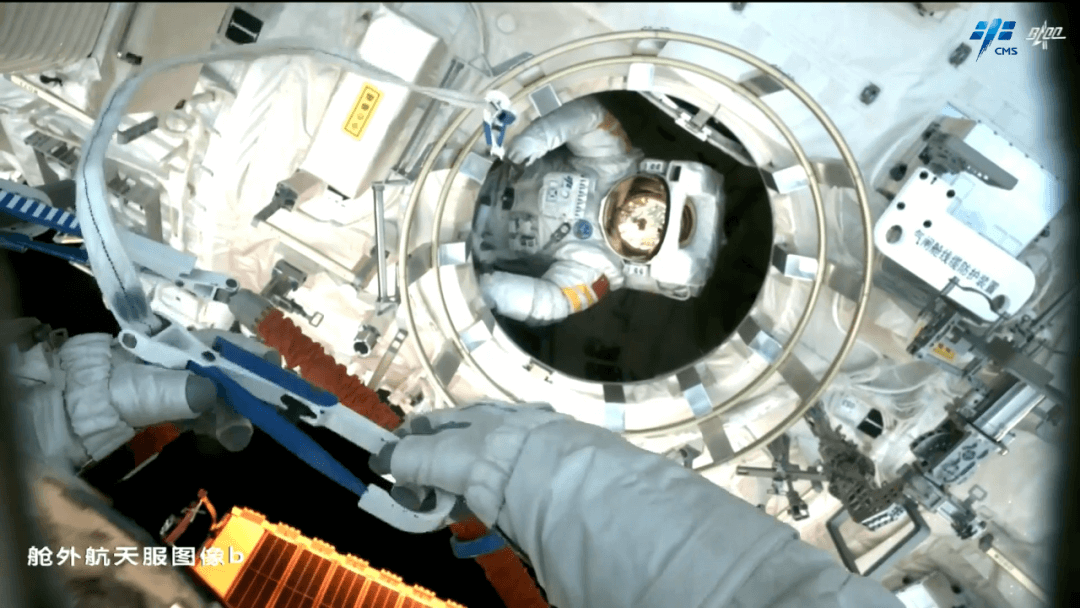
The crew of Shenzhou 16 astronauts successfully completed all the predetermined tasks for extravehicular activities
According to the China Manned Space Engineering Office, at 21:40 Beijing time on July 20, 2023, after about 8 hours of extravehicular activity, astronauts Jing Haipeng, Zhu Yangzhu, and Gui Haichao of the Shenzhou 16 spacecraft worked closely together with the support of the space station's robotic arm to successfully complete all the predetermined tasks of the extravehicular activity. Astronauts Jing Haipeng and Zhu Yangzhu have safely returned to the space station's Wentian experimental module, and the extravehicular activity has been a complete success.
During the astronaut's extravehicular activities, the installation and lifting of the in orbit bracket for the core module panoramic camera B, as well as the unlocking and lifting of the Dream Module panoramic cameras A and B, were completed smoothly and successfully. Astronaut Jing Haipeng, who had flown four times, cooperated from the time capsule of Shenzhou VII to this extravehicular activity, and with 15 years of persistence, fulfilled his dream of 'spacewalking'; Astronaut Zhu Yangzhu became China's first space flight engineer to conduct extravehicular activities.
The successful launch of the Ceres 1 Y6 carrier rocket
At 13:07 Beijing time on July 22, 2023, the Gu Shen Xing 1 Yao Liu carrier rocket was successfully launched from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in China, successfully launching two commercial satellites, Qiankun-1 satellite and Xingdai-16 satellite, into the scheduled orbit for launch.
This mission is the sixth flight of the Ceres I carrier rocket.

China has successfully launched four satellites, including the Four Elephants 01 magnitude
At 10:50 am Beijing time on July 23, 2023, China successfully launched four satellites, Sixiang 01~03 and Galaxy Aerospace Lingxi 03, using the Long March-2D carrier rocket from the Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center. The satellites were successfully placed into the designated orbit and the launch mission was a complete success. The Four Symbols 01~03 satellites are mainly used to obtain remote sensing observation data and provide commercial remote sensing services; The Galaxy Aerospace Lingxi 03 satellite is mainly used for satellite communication technology verification.
This mission is the 479th flight of the Long March series of carrier rockets.

China has successfully launched the Remote Sensing 36 satellite
At 04:02 Beijing time on July 27, 2023, China successfully launched the Remote Sensing 36 satellite into orbit using the Long March-2D carrier rocket at the Xichang Satellite Launch Center, using a one rocket three star approach. The satellite successfully entered its intended orbit and the launch mission was a complete success.
This mission is the 480th flight of the Long March series of carrier rockets

First time in domestic business! The Gravity 1 rocket assisted separation test has been successfully completed
At the end of July, Dongfang Space independently designed and organized two 'Gravitation-1' carrier rocket assisted separation tests at Dongfang Space Port.
This experiment is the first commercial aerospace booster separation test in China. The test fully assessed the timing of booster separation, the compatibility of multiple separation devices, the reliability of bundling structure work, and the coordination of separation process. Both experiments were successfully conducted.